Varicose vein and its Homoeopathic Medicine
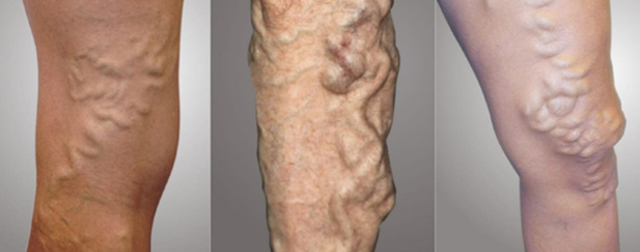
Dilated, tortuous and elongated superficial veins of the limbs are called as varicose veins.
Examples of varicosity
Long saphenous varicosity
Short saphenous varicosity
Oesophageal varices and fundal varices
Haemorrhoids
Varicocoele
Vulval varix and ovarian varix
Clinical examination of a case of varicosity of the leg
Majority of the patient come, with dilated veins in the legs. They are minimal to start with and at the end of the day they are sufficient large because of the venous engorgement.
Dragging pain in the leg or dullache is due to heaviness. Night cramps occur due to change in the diameters of the veins. Aching pain is relieved at night on taking rest or elevation of limbs.
Sudden pain in the calf region with fever and oedema of the ankle region suggests deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
Patient can present with ulceration, eczema, dermatitis, bleeding.
Symptoms of pruritus/itching and skin thickening.
Sign
Inspection ( should be done in standing position)
Dilated veins are present in the medial aspect of the legs and the knee. Sometimes they are visible in the thigh also. Single dilated varix at SF junction is called as saphenous varix. It is due to saccular dilatation of the upper long saphenous vein at the saphenous opening.
Palpitation
1.Cough impulse test (Morrissey test)
This test should be done in the standing position. The examiner keeps the finger at SF junction and patient is asked to cough. Fluid thrill an impulse felt by the fingers is indicative of saphenofemoral incomplete.
2. Trendelenburg test
This test is done in 2 parts
Method
Patient is asked to lie on the cough in the supine position. The leg is elevated above the level of heart and vein emptied. SF junction is occluded with the help of the thumb and the patient is asked to stand. In Trendelenburg 1st, release the thumb or tourniquet immediately. Rapid gush of blood from above downward indicates saphenofemoral incompetence.
Trendelenburg second - The pressure at the SF junction is maintained without releasing the thumb or tourniquet. The patient is then asked to stand. Slow filling of the long saphenous is seen. It is due to perforator in competence.
Investigation
Doppler ultrasound
Duplex ultrasound
Venography
Treatment
Varicose veins can be treated by three methods
1.Conservative line of treatment
Elastic crepe bandage and elevation of leg
2.Injection line of treatment
3% sodium tetradecyl sulphate or 1-2 ml of ethanolamine oleate or hypertonic saline is injected into the column of vein.
Tight elastic compression bandage is applied.
3.Surgery
Trendelenburg's operation
Subfascial ligation of Crockett and Dodd
Subfascial endoscopic perforator surgery.
Homoeopathic Medicine for Varicose veins
- Carbo Veg
- Pulsatilla
- Zincum met
- Aesculus
The selection of homoeopathic remedies based on symptom similarities and doses according to the Susceptibility of patient.
Don't take homoeopathic medicine without any prescription / without any advise of physician.



Comments