ROLE OF HOMOEOPATHY IN UTERINE FIBROID
Uterine Fibroid is the commonest benign tumour of the uterus and also the commonest benign solid tumor in female.
Histologically this tumour is composed of smooth muscle and fibrosis connective tissue, so named as Uterine leiomyoma, myoma or fibromyoma.
Incidence
- It has been estimated that at least 20% of women age of 30 have got fibroid in their womb.
Risk factors of Fibroid
- Nulliparity
- Obesity
- Hyperoestrogenic state
- Black women
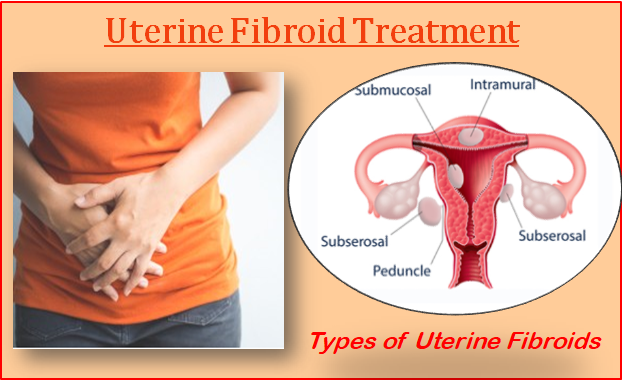
Classification
Types
- Body
- Cervical
1. Body
The fibroids are mostly located in the body of the uterus and usually multiple.
Interstitial/Intramural ( 75%)
Subperitoneal/subserous (15%)
Subserous
Broad ligament
Wandering
Submucous (5%)
Sessile
Pedunculated (polyp)
2. Cervical
Cervical fibroid is rare (1-2%). In the supravaginal part of the cervix, it may be intestinal or sub-peritoneal variety and rarely polypoidal.
Depending upon the position, it may be anterior, posterior, lateral or central.
Interstitial growth may displace the cervix or expand it so much that the external os is difficult to recognise.
All these disturb the pelvic anatomy, specially the ureter.
Anterior
Posterior
Central
Lateral
Clinical Feature
Patient profile
- The patients are usually nulliparous or having long period of secondary infertility. However, early marriage and frequency high even amongst the multiparous women.
Incidence
- Its peak between 35-45 years. There is tendency of delayed menopause.
Symptoms
- The majority of fibroids remain asymptomatic (75%). They are accidentally discovered by the physician during routine examination or at laboratory or laparoscopy.
- The symptoms are related to the anatomic type and size of tumour.
- The site is more important than the size.
- A small submucous fibroid may produce more symptoms than a big subserous fibroid.
Menstrual abnormalities
- Menorrhagia
- Metrorrhagia or irregular bleeding
- Dysmenorrhoea
- Infertility
Uterine
- Distortion and or elongation of the Uterine cavity- difficult sperm ascent.
- Preventing rhythmic Uterine contraction due to fibroids during intercourse-impaired sperm transport.
- Congestion and dilatation of the endometrial venous plexuses-defective nidation Atrophy and ulceration of the endometrium over the submucous fibroid-defective nidation.
- Menorrhagia
- Dyspareunia
Tubal
- Cornual block due to position of the Fibroid.
- Marked elongation of the tube over a big fibroid.
- Associate salpingitis with tubal block.
Ovarian
- Anovulation
Peritoneal
- Endometriosis
Unknown - other
Pain in lower abdomen
- The fibroids are usually painless. Pain may be due to some complications of the tumour or due to associated pelvic pathology.
- Due to tumour
- Degeneration
- Torsion subserous pedunculated fibroid
- Extrusion of polyp
Associated pathology
- Endometriosis
- PID
Abdominal swelling (lump)
- The patient may have a sense of heaviness in lower abdomen.
- She may feel a lumb in the lower abdomen even without any other symptoms.
Pressure symptoms
- The fibroid is the posterior wall may be impacted in the pelvic producing constipation, dysuria or even retension of urine.
Sign
Abdominal examination
- The tumour may not be sufficient enlarged to be felt per abdomen. But if enlarged to 14 weeks.
Palpation
- Feel is firm, more towards hard, may be cystic in cystic degeneration.
- Margins are well-defined except the lower pole which can not be reached suggestive of pelvic in origin.
- Mobility is restricted from above downwards but can be moved from side to side.
Percussion
- The swelling is dull on percussion.
Pelvic examination
- Uterus is not felt separate from the swelling and such as a groove is not felt between the uterus and the mass.
- The cervix moves with the movement of the tumour felt per abdomen.
Investigation
- Ultrasound and colour Doppler (TVS)
- Transvaginal ultrasound
- Saline infusion sonography (SIS)
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Laparoscopy
- Hysteroscopy
- Uterine curettage
Differential diagnosis
- Pregnancy
- Full bladder
- Adenomyosis
- Myohyperplasia
- Ovarian tumour
- TO mass
Complications of fibroids
- Degeneration
- Necrosis
- Infection
Homoeopathic Remedies For Uterine Fibroid
- Phos
- Thuja
- Thlaspi Bursa Pastoris
- Sabina
- Plumbum
Phos
Phos is a great remedy for Uterine fibroid.
Growth of fibroid, submucous type growth under the mucous membrane of uterus which project inside the uterine cavity.
It is usually single in number and sessile.
Due to fibroid, the cavity of the uterus enlarges.
There may be associated endometrial hyperplasia with endometritis.
There is hypertrophy and inflammation of blood vessels of the uterus.
These changes seen after menopause.
Due to overgrowth of fibroids, there is prolapse of uterus with weak, sinking feeling in the abdomen.
Pain in the uterus have tendency to run upwards.
Due to inflammatory conditions there are Stitching and throbbing pains in uterus or vagina.
Menses are profuse and too late.
Leucorrhoea is acrid in nature, present instead of menses.
Desire for cold water, but vomits it out as soon as it gets warm in stomach.
In general all symptoms are relieved by warmth in stomach and aggravated by cold.
Thuja
Thuja is a very important remedy for Uterine fibroid.
Polypoid growth of the uterus turns into cauliflower like growth which bleeds easily.
Due to excess of blood supply to fibroids there is congestion of Uterine wall.
This cause profuse bleeding with stitching pains in abdomen.
Severe backache while walking.
Menses are too short and too early preceded by profuse urination.
Due to the presence of fibroid on urinary bladder there is frequent urging to urinate.
It is best suited to fibromyoma of uterus.
This increase in frequency of micturation, usually at night times, is characteristic of Thuja lady.
She has history of sexually transmitted disease with thick, gleety discharges from urethra with burning.
Modalities
Aggravated in the morning, heat of bed
Better in open air, warmth in general, by movement.
Thlaspi Bursa Pastoris
This remedy is used in the disease of uterus like fibroid of uterus, carcinoma of uterus with profuse haemorrhage, usually frequent.
Haemorrhage in the form of clots.
Pain in the Uterine region due to overgrowth.
Intense backache are general bruised soreness.
Lady complaints of various Uterine diseases and suppression of the same by the use of medicines.
Metrorrhagia, too frequent, copious haemorrhages with violent Uterine colic.
Every alternate period is very painful and she bleeds profusely.
Leucorrhoea before and after menstruation.
It is bloody, dark and offensive.
There is frequent desire for urination.
She has frequent desire to urinate.
Dysuria
Sabina
Sabina is covered under sycotic miasm, thus lady complaints of overgrowth in the Uterine region.
In the carcinoma of uterus,she has cauliflower like growth which usually occurs by direct spread.
Menstrual cycle are disturbed.
Menses are profuse and blood is bright red in colour.
Uterine pains extend up to thighs.
Pain from sacrum to pubis is characteristic symptom of Sabina lady.
Discharge of blood between periods with sexual excitment.
Uterine haemorrhage is partly clotted and aggravated by least motions.
Violent pulsation with sense of fullness in the peripheral organs.
Uterine fibroids are usually the cause of menorrhagia at the climacteric age.
Profuse leucorrhoea and discharge of bloody.
Uterine haemorrhage is partly clotted and aggravated by least motion.
Modalities
Aggravated by least motion, warmth in general, hot air, hot climate.
Better by cold fresh air, rest.
Intense colicky pain in abdomen at the time of menses, these pains are associated with bearing down or labour like pains.
Pain transverse from vagina to uterus.
Discharge of blood between periods with sexual excitment.
Plumbum
It is best suited remedy for Uterine fibrous.
Patients are climacteric age group.
Bleeding probably might due to Fibroids of uterus or due to systemic disease.
Excessive colicky pain radiating to uterine region.
There is sensation of a string pulling from abdomen to back.
Dark clots difficult to expel from cervical os, thus there is severe pain in abdomen.
Modalities
Aggravated after movement, at night times.
Better by hard pressure.
The selection of homoeopathic remedies based on symptom similarities and doses according to the Susceptibility of patient.
Don't take homoeopathic medicine without any prescription / without any advise of physician.



Comments