ROLE OF HOMOEOPATHY IN HYPERTENSION
It is a condition characterized by an increase in the arterial pressure of individuals. It is most common cardiovascular disease all over the world. It is a clinical condition in which there is persistence elevation of blood pressure by above the lower limits & depends upon the age & sex.
Higher the blood pressure, higher is the risk of complications like stroke, renal failure, myocardial infaraction.
Classification of blood pressure according to WHO
| Stages | Systolic | Diastolic |
| Stage 1st "Mild" | 140 - 159 | 90 - 99 |
| Stage 2nd "Moderate" | 160 - 179 | 100 - 109 |
| Stage 3rd "Severe" | > 180 | > 110 |
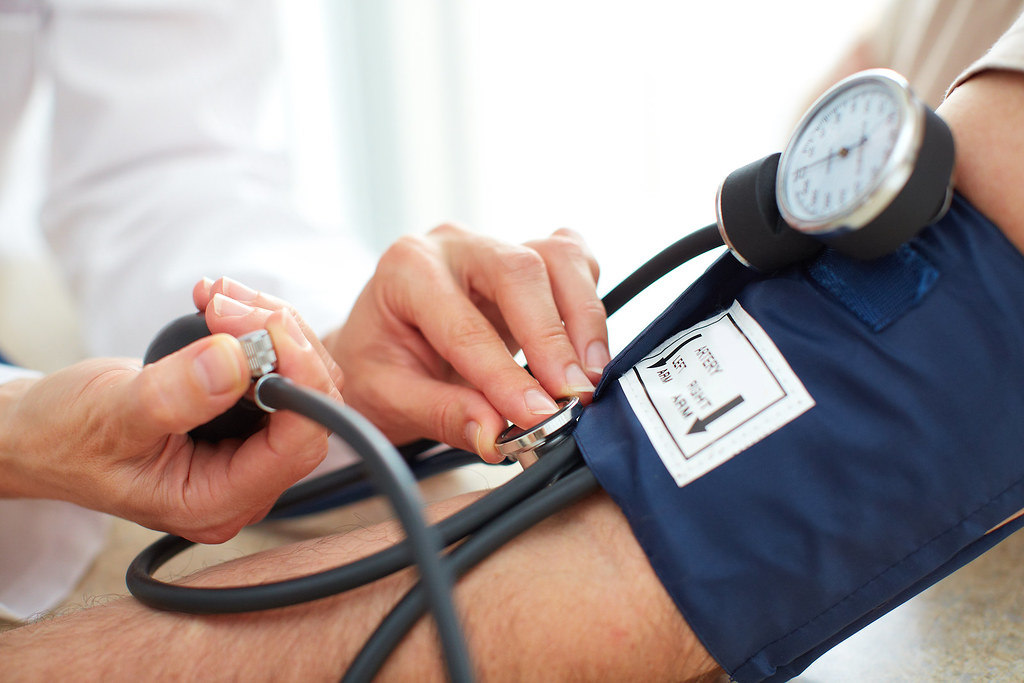
- Blood pressure of an individual is measured by used an instrument known as sphygmomanometer.
- Hypertension is a life style disorder. It is a global problem. In 'India' it is estimated to range "4 - 8%" & trend is increase due to life style.
- A recent report indicates that nearly "1 Billion Adult" globally had HTN in 2000 & this is predicted to increase to "1.56 Billion" by 2025.
- According to WHO (World Health Organization) blood pressure should be recorded in the sitting position of the patient only one (either right or left) to be used consistently 'korot koff sound' is 1st heard is considered as systolic pressure and at which the K sound disappears, as diastolic pressure.
- According the expert of WHO committee at least 3 reading should be taken over a period of '3 minutes' and the lowest reading is recorded hypertension is classified into two types
Primary Hypertension - When the cause is unknown. This accounts for nearly 90 percent of cases.
Secondary Hypertension HTN - when the cause is known such as disease kidney tumor of adrenal gland ,consumption of drugs like steroids oral pills congenital narrowing of the aorta. This accounts for about 10 percent of all cases.
| Primary
Hypertension | Secondary
Hypertension |
| Primary Hypertension also known as essential HTN
when the causes are generally unknown. | Secondary Hypertension is when the causes is
known it is called as secondary hypertension. |
| 85 - 90 % of all cases | 10 % of all cases |
| Essential Hypertension | |
Etiological classification of primary Hypertension.
| Etiological classification of
secondary Hypertension 1. Renal
2. Endocrine
3. Coarctation of aorta 4. Neurogenic |
Hypertension is the silent killer of mankind, most suffer (85%) are asymptomatic and hence early diagnosis in a problem. The dividing line between normal and abnormal blood pressure is arbitrary because blood pressure is dependent upon many factors like age, race, sex.
Target Blood Pressure
The target blood pressure is <140mm hg systolic and <90mm hg
- For diabetics or chronic renal failure blood pressure should be
<130 mm hg systolic, <80 mmhg diastolic
- For diabetics with chronic renal failure blood pressure should be
<125 mmhg systolic, <75mm hg diastolic.
Hypertension Emergencies (Malignant Hypertension)
It is characterized by severe elevation in blood pressure (> 180/120 mm hg) with evidence of impending or progressive target organ dysfunction they requires immediate blood pressure reducing (papilledema, retinal exuadates, retinal hemorrhages, nephropathy, hypertensive encephalopathy, intracerebral hemorrhage, acute myocardial infaraction, acute left ventricular failure with pulmonary edema, unstable angina pectoris, dissecting aortic aneurysm, eclampsia.
Hypertensive Urgencies (Accelerated Hypertension)
It is associated with several elevation in blood pressure without progressive target organ dysfunction (e.g. Upper level of stage 2nd hypertension associated with severe headache, shortness of breath, epixtaxis). Retinal damage may be present but without papilledema.
Isolated Systolic Hypertension
When systolic blood pressure >140 mm of hg and diastolic blood pressure <90 mmhg. It is seen in predominantly in elderly due to arteriosclerosis. It may fluctuate from time to time, higher in morning, lower at night.
Pulse Pressure SBP - DBP (normal 30 - 60mmhg)
Mean Blood Pressure - 2/3 DBP + 1/3 SBP
White Coat Hypertension - The patient's BP is high when measured by a professional but is normal when measured in casual circumstance (at home). It is dignosed by 24 hours ambulatory BP monitoring.
Labile Hypertension - The patient is hypertension at one time and normotension at another time.
Risk Factor of Essential Hypertension
- Age - Usually the prevalence of hypertension is high above 40 years of age .its prevalence rises with age.
- Sex - Young age - during young age there is no difference in hypertension in both genders.
Middle age - males are preponderance.
Later age - In later life women are more prone, may be because of post-menopausal changes.
- Genetic factor - If both parents are hypertensive offsprings have 45 % possibility of developing hypertension and if the parents are normotensive, the possibility is only 3 %.
- Ethnicity - Study have shower higher blood pressure levels among black people than among whites.
Racial and environmental factors
Surveys in the us have revealed higher incidence of essential hypertension in African American than in whites. A no of environmental factors have been implicated in the development of hypertension including salt intake, obesity, skilled occupation, higher living standard and individuals under high stress.
Other risk factor
Other factors which are the alter the prognosis in hypertension include - smoking, excess of alcohol intake, diabetic mellitus, persistently high diastolic pressure above normal and evidence of end - organ damage (i.e heart, eye, kidney, nervous system).
The pathogenetic mechanism in essential hypertension is explained by many theories
- High level (plasma level) of catecholamines
- Increase in blood volume i.e arterial overfilling (volume hypertension) and arteriolar concentration (vasoconstrictor hypertension).
- Increased cardiac output.
- Low renin essential hypertension found in approximately 20%patients due to altered responsiveness to renin release.
- High renin essential hypertension seen in about 15% cases due to decrease adrenal responsiveness to angiotensin 2nd.
Effects of hypertension
Systemic hypertension causes major effects in three main organs heart and it's blood vessels, nervous system and kidney. The renal effects in the form of benign and malignant nephrosclerosis. The organs are damaged by long standing hypertension.
1.CVS - Increased myocardial work leads to concentric hypertrophy of left ventricle, angina pectoris and accelerated coronary artery disease. There is systolic as well as diastolic dysfunction.
2.Kidney - progressive arteriosclerosis involves both the efferent and afferent renal arterioles and capillaries of glomerular tuft. The leads to compromise in the renal function, shrinkage of kidney, proteinuria.
3.CNS - hypertension may cause micro-aneurysms(Charcot bouchard aneurysm ) which may rupture and cause cerebral hemorrhage. Accelerated atherosclerosis may cause cerebral thrombosis, embolism and infarction cerebral arteriolar spasm may cause hypertension encephalopathy.
4.Fundus - Keith Wagner classification.
| Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | Grade 4 |
| Mild generalized arteriolar attenuation. | Deflection of veins at AV crossing (AV nickling) + marked generalized arteriolar attenuation. | Grade 2 + copper wire + cotton woolspot + flame
shaped hemorrhage + hard exudate. | Grade 3 + silver wire + papilledema. |
Clinical feature of hypertension
Symptoms due to hypertension
Headache - The occurs usually in the morning hours .It is throbbing and usually frontal .
Dizziness - The patient feels unsteady.
Epistaxis - This is occur due to increased pressure causing rupture of the capillaries of nose .The bleeding would reduce the circulating volume ,and lower bp ( nature way of lowering the BP and prevention of the hemorrhage in the vital organs).
Symptoms due to affection of the target organs
CVS
- Dyspnea on exertion
- Anginal chest pain
- Palpitations
Kidney
- Hematuria
- Pocturia
- Polyuria
CNS
- Transient ischemic attacks with focal neurological deficit.
- Hypertensive encephalopathy (Headache, Vomiting, Convulsions, Unconsciousness focal neurological deficit).
Retina
- Blurred vision or sudden blindness.
Symptoms due to underlying diseases
- Edema and puffy face - acute nephritis.
- Weight gain, hirsutism - Cushing's syndrome.
- Weight loss, tremors, palpitation and sweating - hyperthyroidism/pheochromocytoma.
- Weakness - primary hyperaldosteronism.
- Joint pains, bronchospasm, peripheral vascular disease symptoms - poly a rteritis nodosa.
Signs
General examination
- Moon face, buffalo hump and truncal obesity - Cushing syndrome.
- Puffy eyes, rough skin, obesity - myxedema.
- Tremors, Tachycardia, Exophthalmos, thyroid dermopathy and goitre - hyperthyroidism.
- Prognathism, Clubbed hand, Coarse features - acromegaly.
- Pigmentation - Neurofibromatosis.
- Radio femoral delay and collateral vessels over the chest wall - coarctation of aorta.
- Weaker left radial - preductual coarctation.
- Water hammer pulse - aortic incompetence.
Cardiological symptoms
- Cardiomegaly.
- Third and fourth heart sound gallop.
- Loud second heart sound.
- Early diastolic murmur - due to AI.
Respiratory symptoms
- Basal crepitations - LVF.
- Rhonchi - LVF, Polyarthritis nodosa.
- X-ray chest for heart size.
- ECG for LV hypertrophy and evidence of IHD.
- Echocardiogram for LV systolic and diastolic function.
- Urinalysis - proteinuria >200mg/day and hematuria suggest renal involvement, Further investigation include serum creatinine, renal sonography, isotopic renogram, renal biopsy.
- Rib notching suggests coarctation of aorta.
- Mediastinal widening suggest aortic dissection.
- Polycystic kidney
- Tumour of kidney
- Adrenal tumour
- Renal calculi
- Pheochromocytoma
Treatment of hypertension
- Salt restriction - modest sodium restriction to up to 110 mmoles / day (2.4g sodium or 6 g sodium chloride) is effective in controlling hypertension in mild to moderate hypertension because sodium and water retention is involved in large proportion of hypertensive.
- Weight reducing - In over weight persons, reducing of 1 kg may reduce 1.6/1.3 mmhg bp.It also modifies other cvs risk factor like diabetes and dyslipidema. BP is lowed by - reduced circulating volume which reduce venous return and cardiac output.
- Reduced symptomatic activity and plasma non - epineohrine - reduction in hyperinsulinemia.
- Stop smoking - smoking acutely raises B.P. In addition,it is an independent and most important reversible coronary risk factor.since tolerance develops to nicotine -induced hemodynamic effects, chronic smoking may not be associated with high BP.
- Diet - Lactovegeterian diet and high intake of polyunsaturated fish oil have high potassium levels and lower BP by.
- Increased sodium excertion.
- Decreased sympathetic activity.
- Decreased renin - angiotension secretion and direct dilatation of renal arteries.
- Adequate calcium, magnesium intake should be maintained in the diet.
- Saturated fat and cholesterol intake should be reduced for overall cardiovascular health.
- Limit of alcohol intake
- Relaxation - various forms of relaxation like yoga, biofeedback and psychotherapy lower BP, especially in those with sympathetic.
- Regular exercise
- Diuretics - oral diuretics were the most widely used anti - hypertension agents.They are effective alone in 50% of mild hypertensive .Thiazides are very effective. They are well tolerated and need to be give only once a day .The enhance the potency of other anti-hypertensive.They act by reducing extracellular fluid volume and cardiac output and they help to counteract the hypertensive effect of high salt intake. They can aggravated diabetes by suppression release of insulin due to hypokalemia.Hyperlipidemia, hypomagnesemia, hyponatremia, hypokalemia, hyperuricemia may occur. Now they are usually used in combination therapy.
- Beta blockers - Reduce cardiac output and lower BP but raise the peripheral resistance on a acute administration (which increases BP). However, on chronic administration, BP falls to pretreatment levels .In mild to moderate hypertension, it lower the BP > 50% patients.Drugs withdrawal, if needed, should be done slowly, or rebound hypertension may occur. They can be combined with diuretics, calcium blockers, ace inhibitors and vasodilations .They may be precipitate bronchospasm, cardiac failure, peripheral vascular disease, impotence and depression.
- Natriuresis and diuresis due to increased GFR and decreased aldosterone.
- Anti-angios tensin - 2 effect
- Direct negative effects inotropic effect which lower cardiac output.
- Peripheral vasodilation
- Nifedipine was the commonest used calcium blockers. Now Amlodipine is replacing it. Felodipine, nicardipine, nitrendipine and clinidipine are other useful calcium blockers. These drugs are especially useful in elderly hypertensive flushing, headache, palpitation, edema, hypotension may occur.
- ACE inhibitors - renin released from the kidney act on circulating angiotensin ogen to produce angiotensin 1st, which is converted to angiotensin second by converting enzyme. Angiotensin second is a potent vasoconstriction and its stimulates aldosterone, which retains sodium and cause hyper-tension ACE inhibitors acts by inhibiting the converting enzyme preventing the formation of angiotensin second and lowering the BP. They also act by reducing the degradation of bradykinin-a potent vasodilation, which lowers the BP. ACE inhibitors causes regression of ventricular hypertrophy, attenuation of reperfusion injury induced ventricular arrhythmias, preload and after load reduction and coronary vasodilation. These drugs have no adverse effects of lipid, urine acid glucose metabolism. They lower the BP by 15-25%.Diastolic pressure is lowered more than systolic pressure. Concomitant sodium restriction and diuretics further lower by 15-25%. ACE inhibitors are useful in renovascular hypertension. High angiotensin second is however required to maintained adequate filtration pressure behind the stenotic lesion. ACE inhibitors decrease perfusion pressure and lead to azotemia. Thus they are contraindicated in bilateral renal artery stenosis. These drugs are useful in hypertensive diabetic because of neutral effect of carbohydrates metabolism. In addition they decrease microalbuminuria.
- Captopril also improve insulin sensitivity. It has a short duration of action and use for cardiac failure.
- Enalapril, Perindoril, Ramipril, etc. are longer acting. ACE inhibitors and useful in hypotension. Tissue specific ACE inhibitors like Quinapril, ramipril, perindopril, fosinopril are available.
- Angiotensin second blockers are useful in patients with ACE inhibitors - induced cough and in elderly hypertensive Losartan, Isbesartan, valsartan, candersartan are available .
- Alpha blockers - Adrenergic stimulation of alpha 1 receptors in smooth muscles cause vasoconstriction and hypertension. Alpha blockers attenuation vasoconstriction and there by decrease vascular resistance and BP Prazosin was the first alpha blockers with short duration of action.
- Terazosin ana doxazosin are longer acting once a day alpha blockers. The efficacy can be enhanced by the concomitant used of diuretics. The most dramatic adverse effects is the 1st dose postural hypotension/syncope. Alpha blockers also have other beneficial effects like lowering the lipids, regression of left ventricular hypertrophy enhancing insulin sensitivity (hence idea for diabetic hypertensive) and releif of obstructive symptoms in benign prostatic hypertrophy.
- Vasodilators - These drugs act on the arteriolar smooth muscles, causing vasodilation and lowering BP. However, reflex tachycardia and increase in cardiac output limits its usefulness in severe coronary artery disease. These effects can be reduced by combining hydralazine with beta blockers. Minoxidil is the other vasodilatior whose usefulness is limited due to hirsutism in females. Diazoxide and Nitroprusside are parenteral vasodilators useful in hypertensive emergencies.
HOMOEOPATHIC MEDICINE FOR HYPERTENSION
The selection of homoeopathic remedies based on symptom similarities and doses according to the Susceptibility of patient.
Don't take homoeopathic medicine without any prescription / without any advise of physician



Comments