ABOUT RENAL CALCULI ITS TYPES CAUSES AND ITS HOMOEOPATHIC REMEDIES
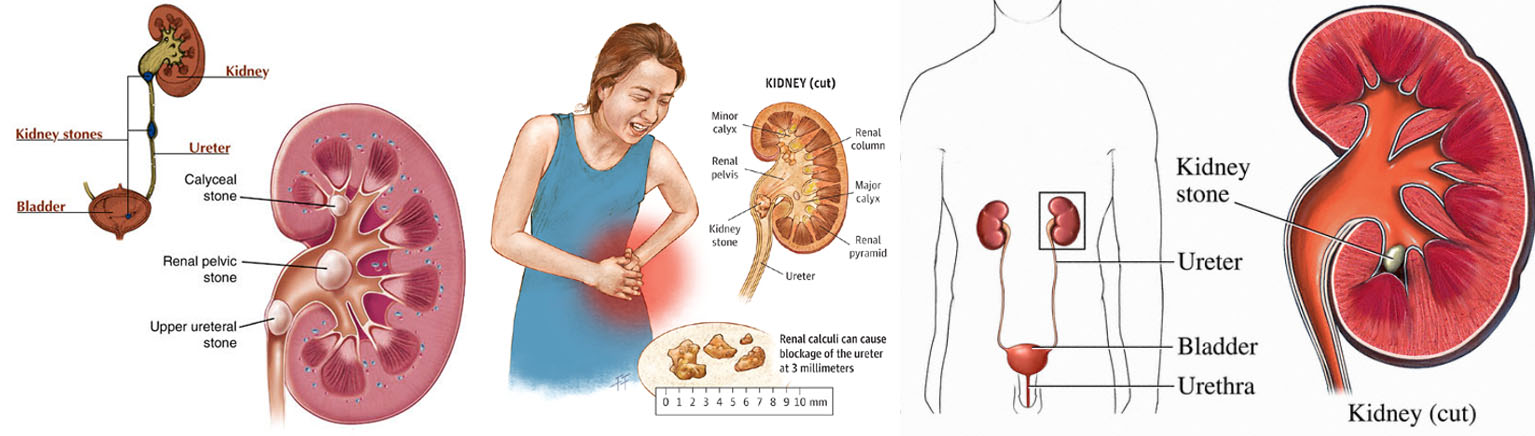
Renal calculi
Aetiology
1. Infection
- E.coli
- Pseudomonads
- Klebsiella
2. Hot climate
- It cause increase in concentration of solutes, resulting in precipitation of calcium which forms calcium oxalate stone.
3. Dietary factory
- Diet rich in red meat,fish,eggs can give rise to aciduria.
- Diet rich in calcium, tomatoes,milk,spinach,rhubarb produces calcium oxalate stone.
- Diet lacking in vitamin A causes desquamation of renal epithelial which precipitates calcium and alters it and stone formation occur.
4. Metabolic cause
- Hyperparathyroidism increase serum calcium levels resulting in hypercalcinosis and pelvic stones
- Gout increase uric acid levels and causes multiple uric acid stones.
5. Immobilisation
6. Decrease urinary citrates
7. Inadequate urinary drainage
8. Randall's plaques
Types of Renal Stones
1. Calcium Oxalate Stone
- Called as mulberry calculi
- Common type of stone
- It is irregular having sharp projections
- Oxalate stone is hard and single
- Produce haematuria very easily, resulting in disposition of blood over the stone giving a dark colour to the stone.
- It occur in infected urine
- Contains alternate layer of calcium and bacterial vegetation.It is visualised in plain X-ray KUB.
2. Phosphate Stone
- Smooth,round
- Consist of triple phosphate of calcium, magnesium and ammonium.
- Dirty white to yellow in colour
- Commonly occur in renal pelvic and tends to grow in alkaline urine.
3. Uric Acid stone
- Multiple,small, hexagonal,faceted, yellow coloured
- Contains calcium oxalate which makes them opaque.
- Pure uric acid stones are radiolucent.
- Occur in acidic urine
- Common in the patients who consume red meat.
4. Cystine calculus
- Cystinuria is an inborn error of metabolism which occur due to decreased resorption of cystine from the renal tubules.
- Occurs in young girl in puberty
- Increased excretion of cystine in urine results in cystine calculus
- Stone hard and radio-opaque due to sulph content.
Clinical Feature
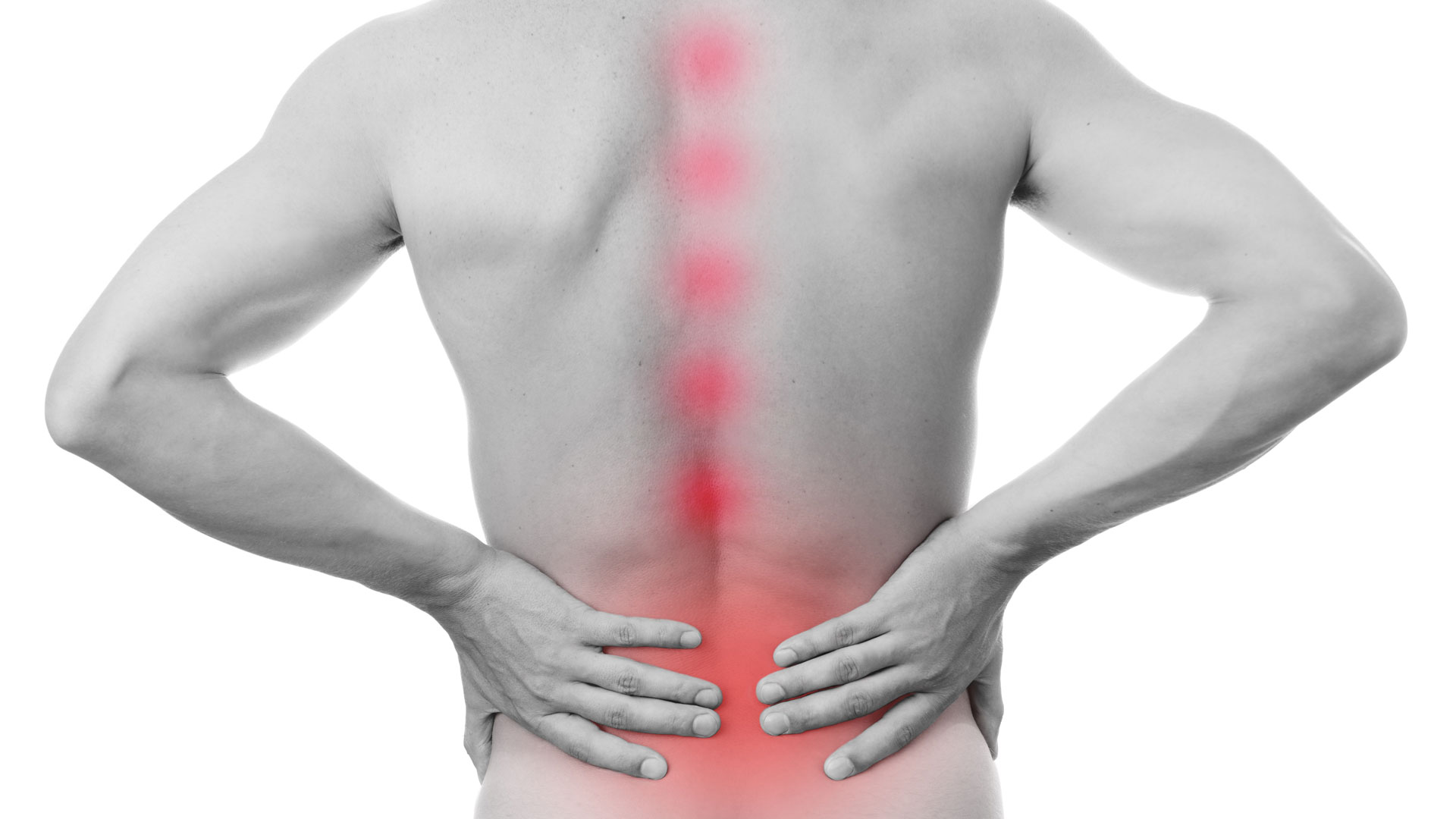
1. Renal Pain
Dull aching to pricking type of pain posteriorly in the renal angle formed by the sacrospinalis and 12th rib. Murphy's kidney punch test demonstrate tenderness at renal angle.The same pain may some times be felt anteriorly in the costal margin. Hence,it is described as costovertebral pain.
2. Ureteric colic
When the stone is impacted in the pelviureteric junction or anywhere in the ureter,it results in severe colicky pain originating at the loin and radiating to the groin,testicles, vulva and medial side of the thigh.This may be associated with strangury.The reffered pain is due irritation of the genitofemoral nerve.
3. Haematuria
It is common with renal stone because the majority of the stone are oxalate stones. The quantity of blood lost is small but it is fresh
4. Recurrent U.T.I.
Fever with chills and rigors, burning micturition,pyuria may occur,along with frequency of micturition.
5. Guarding and rigidity
In Back and abdominal muscles during severe attack of pain.
Complications
- Calculous hydronephrosis
- Calculous pyonephrosis
- Renal faliure
Investigations
- Blood urea and creatinine
- Plan X-ray KUB
- USG
- IVP
- Urine culture and sensitivity
Treatment
The treatment of renal stone is divided into non operative and operative treatment.
1.Non-operative treatment
- Small stones less than 5 mm in size pass off with intake of copious amount of fluids and at times forced diuresis.
- Intravenous hydration followed by intravenous frusemide may help pass the stone spontaneously.
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy(ESWL).
- After cystoscopy a ureteric stent (Double J stent) is placed into the ureter on the side of a large renal stone. Shock wave are generated (around500-1500shock wave) with blast the stones.
- The stones get crushed and most of the stones will come out by the side of the sent.
2. Operative treatment
(A) Endoscopic procedures
- Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL)
(B) Open procedures
- Pyelolithotomy
- Nephrolithotomy
- Extended pyelolithotomy
- Pyelonephrolithotomy
- Partial nephrectomy
- Nephrectomy
(C) Special situation
- Bilateral renal stone -Kidney with better function has to be operated 1st. 1-2 weeks later,the opposite side can be operated.
- If there is pyonephrosis with a severe degree of fever,pain and tenderness, nephrostomy is done and a tube drain is placed in the pelvis of kidney for drainage of pus and urine.
Homoeopathic Medicine For Renal Calculi
- Berberis vulgaris
- Sarsaparilla
- Cantharis
- Pareira brava
- Ocimum canum
Berberis vulgaris
Sore pain in the region of kidney.
Soreness of muscles of back
The pain travels from the lumbar region to front of the abdomen.
Pain shift from one place to another
Burning and stitching pains
Kidney region is sensitive and tender to touch
Little or small calculi are formed in the pelvis of kidney.
Urine is dark,turboid with excessive sedimentation.
There is also catarrhal condition of the bladder with smarting burning pain. Patient has constant desire for urination
Vesicle calculus occur due to deposition of urinary salt upon the foreign body in bladder.
Frequency of micturition is mostly seen in bladder stone.
Urine is hot, dark,or blood red in colour.
Bruised sensation in kidney region and small of back.
Modalities-Aggravation from movement, lying on abdomen,large quantity of cold water.
Sarsaparilla
It is a very good remedy for renal calculi of right side.
Agonising pain in right kidney region from back to front.
There is great muscular spasm of the lumbar muscle,which makes the patient bend double,lies in knee chest position.
In attack there is severe agonising pain due to which the patient tosses in the bed.
Patient cries out due to pains.
Urine dribbles away when sitting
Patient passes small calculi with urine.
Associate with blood painful retention of urine.
Patient shouts
Increased frequency of micturition
Catarrhal condition of urinary tract, kidney,ureter and bladder
Violent pain at the end of urination.
Scanty and slimy urine.
Urine flow freely with standing
Modalities- Aggravated from warm food,and drinks,night,after urination.
Better by Hot, external application and cold drinks and water.
Cantharis
Intolerance urging and tenesmus in region of kidney.
Nephritis with high colour urine
Violent paroxysmal of cutting and burning in whole region with painful urge to urinate.
Cantharis patient passes urine drop by drop.
Intolerable tenesmus
Cutting pain in kidney region and in ureter after urination.
Constant desire to pass urine.
Due to constant desire to urine is scanty and high coloured.
Haematuria
Burning in mouth, after talking
Vomiting of watery fluid during left ureteric colic.
Urine scalds and due to inflammation passes drop by drop.
Modalities- Aggravation from touch, micturition, drinking of cold water
Better by rubbing and pulling the organs.
Pareria
Dysuria
Patient has to press and strain while micturating. Useful for bladder stones.The stones caught in trigone of bladder which blocks the passage of urine,and so retension and distension of bladder.
Urine passes drop by drop with sensation of fullness of bladder.Violent pain in bladder and sometimes at coccyx.
Due to left kidney stones there is pain reffered in left testis which is drawn up.
Pain on medial side of the thighs.
Paroxysm of violent pain with strangury.
Can only passes urine when on his knees, pressing head firmly on floor for 10-20 minutes.
Modalities-Aggravation at 3-6A.M.
Ameliorate during day time.
Ocimum Can
Turbid urine is highly acidic.
Formation of spike like crystals of uric acid.
Turbid,thick,purulent,bloody deposits and white albuminous sedimentation.
Urine is saffron in colour.
Crampy pain in the kidney region.
Severe renal colic with nausea and sense of vomiting.
Patient rolls in bed during the attack.
After attack urine is brick red or large quantity of blood in urine.
Thick purulent urine with intolerance smell of musk.
It is in calculus of kidney,ureter and bladder.
Uric acid diathess.
Red sand in urine is characteristic.
Swelling of glands, especially of right sided.
The selection of homoeopathic remedies based on symptom similarities and doses according to the Susceptibility of patient.
Don't take homoeopathic medicine without any prescription / without any advise of physician.



Comments