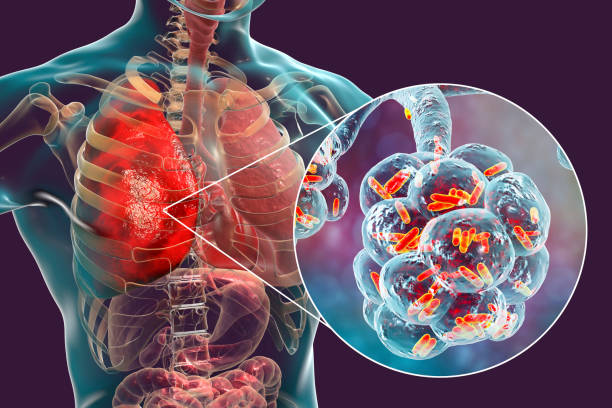
About Pneumonia
Inflammation of lung parenchyma including- terminal airway, alveolar (lobar-20%), interstitial space(10%).
Infection that inflames air sacs in one or both lungs, which may be fill with fluid.
With pneumonia the air sac may fill with fluid or pus.
Classification
Classification according to causitve agent
Bacterial
Streptococcus pneu
H.Influenza
Staphylococcus aureus
E coli
Klebsiella
Chlamydia Pneumonia
Rickettisal
Mycoplasma pneumonia
Viral
Measles
H1N1
Influenza
Parasitic
Entamoeba histolytica
Pneumocytes carini
Fungal
Histoplasma capsulatum
Classification by site
Lobar(20%) -alveolar or air space pneumonia
Lobular (70%) -bronchopneumonia
Interstitial (10%)
Acute lobar pneumonia
Diffuse inflammation affecting part of lung(part/entire lobe) usually lower lobe.
Predisposing cause
Age<50yrs (50%case)
Sex-both
Season- winter and rainy season
Devitalising condition
Addiction to alcohol and smoking
Overcrowding
Poor sanitation
Respiratory disease-influenza,chronic bhronitis, bronchiectasis, cystic fibrosis.
Inhalation of foreign materials
Drug-steroids
Clinical features
- Temperature high
- Pain in the RT side of chest in about 70% of cases
- Dyspnea
- Cough
- Tenacious sputum
- Malaise weakness
- Headache
- Aches all over the body
- Delirium
- Confusion due to toxaemia
Sign
- Cyanosis
- Pulse rapid
- Respiration hurry
- Pulse respiration ratio markedly altered 2:1
- Temperature high
- Inspection restricted movement of affected part of chest
- Percussion woody dullness over the affected part
- Auscultation breath sound is tubular in type
Investigation
Blood leucocytosis
Sputum culture- causative organism
X-ray of chest show opacity over the affected lesion.
Blood culture positive.
Management
Bed rest
O² inhalation (nasal catheter)
Penicillin 1mega unit IM6 hourly
Codeine phosphate 15-30mg to relieve cough
Diazepam
Plenty of fluide
Electrolyte.
Lobular Pneumonia
Bacterial Pneumonia (70%)
Widespread pneumonia
Patcy in distribution proceded by bronchial infection.
Symptom
Low grade fever
Remittent type
Distressing cough
Purulent expectoration
Breathlessness
Treatment
- Postural drainage
- O² inhalation
- Syrup pholcodin 2-4cc
- Antibiotics- Ampicillin, tetracycline.
The selection of homoeopathic remedies based on symptom similarities and doses according to the Susceptibility of patient.
Don't take homoeopathic medicine without any prescription / without any advise of physician.



Comments