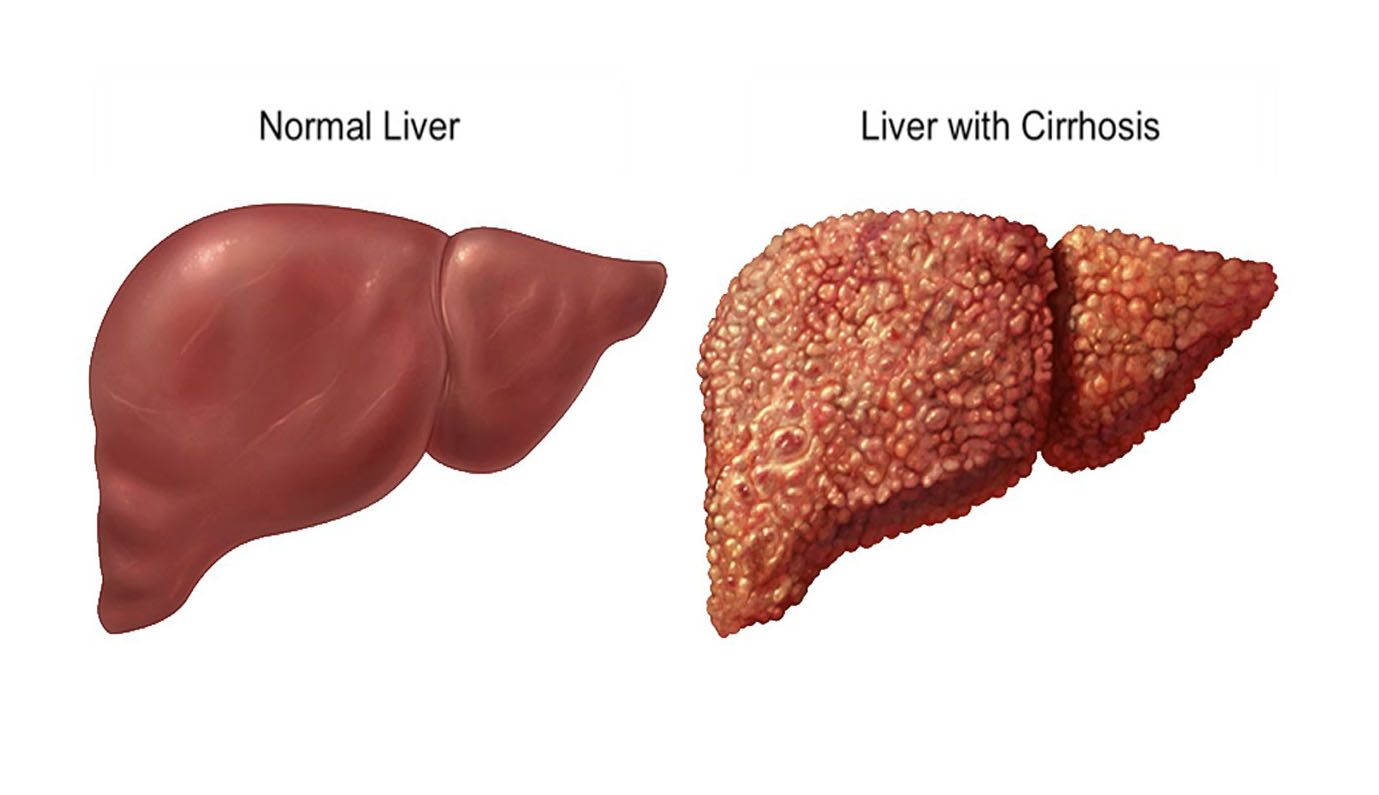
About Cirrhosis of Liver
It is the condition of destruction of hepatic cell.
Cirrhosis of liver is a diffuse disease having 4 features following.
1.It involve the entire liver.
2. The normal lobular architecture of hepatic parenchyma is disorganised.
3. Formation of nodules separated from one other by irregular bands of fibrosis.
4. It occur necrosis and regenerative nodules.
In western world, cirrhosis of liver is one of the ten leading cause of death.
Type
Micronodular
Macronodular
Mixed
Micronodular
Nodules less than 3mm
Chronic alcoholism is commonest cause.
Involvement of every lobule of whole liver.
Uniform, regular connective septa.
Macronodular
Nodules more than 3mm
Chronic hepatitis is commonest cause.
Liver surface is grossly distorted.
Mixed
Shoe the feature of both micronodular and macronodular cirrhosis.
Aetiology
Alcoholic cirrhosis
Post necrotic cirrhosis
Post viral cirrhosis
Biliary cirrhosis
Cardiac cirrhosis
Wilson's cirrhosis
Glucogen storage disease
Intestinal bypass surgery
Galactosemia
Idiopathic cirrhosis
India childhood cirrhosis
Pigment cirrhosis
Drug induced cirrhosis
Clinical features
Low grade fever
Weakness
Fatigue
Weight loss
Anorexia
Nausea
Vomiting
Upper abdominal discomfort
Abdominal distention
Menstrual irregularities
Haemorrhagic tendency
Bleeding piles
Haematemesis
Gradual swelling of abdomen and feet.
Diarrhea
Constipation
Sterlity
Impotense.
Sign
Age more than 30 years
Hepatic face
Anaemia
Jaundice
Spider angioma
Oedema
Ascites
Haemorrhage
Cyanosis
Tongue pale and dirty
Bloated abdomen
Umbilicus everted
Abdominal vein prominent
Apex beat- displaced upward
Murmur- soft systolic murmur
Falling of public and axillary hair due to lack of detoxification of oestrogen.
Liver enlarged
Parotid enlarged
Clubbing
White nail
Complication
- Portal hypertension
- Ascites
- Bleeding piles
- Anaemia
- Haemorrhage
- Hernia
Management
Bed rest
Removal the causative agent
High protein diet
Vaccination (hepatitis A and B, influenza, pneumococus)
Blood transfusion
Diuretic oral thiazide diuretics
Na should be restricted in the diet upto 400-800mg/day.
Liver transplantation.
Investigation
1.X-ray- hepatomegaly
2. CBC- Anaemia, leucopenia
3. Liver function test
4. Liver biopsy
5. Portal venography- dialated portal vein
6.Ultrasound- splenic enlargement, ascites, small size liver
7. Metabolic abnormalities
8. Hepatitis B and C marker
9. Prothrombin time
10. Urine- urobilinogen
11. Ba oesophagogram- earthworm like filling.
The selection of homoeopathic remedies based on symptom similarities and doses according to the Susceptibility of patient.
Don't take homoeopathic medicine without any prescription / without any advise of physician.



Comments